Religions: The faith journey of the Turks
The religious beliefs of the Turks, which started with Tengrism (Göktanrı), met with the monotheistic religions after Manichaeism and Buddhism, and continued their beliefs in 7 religions.
In the 21st century, more than 35 Turkish tribes and communities dispersed in Asia and Europe maintain their beliefs in 5 religions:
Islam………………..17 tribes of
Christianity………………….11 tribes of
Shamanists……………….4 tribes of
Buddhist …………………..3 tribes of
Jews……………………….. 2 sizes
Half of the 35 tribes preferred Islam, three quarters preferred Islam-Christianity, while the Asian beliefs in the form of Shamanism-Buddhism were preferred by 20% of the tribes. FAITH JOURNEYS OF THE TURKS Tengri The first word identified in Turkish is Tengri (God). It is seen that Turks have strong beliefs and the conceptual framework is ancient and strong.
Atheism would later jump over the Yakut Turks to the Americas.
The Turks have also transformed the belief world of the Chinese with their belief in the Gods of Heaven.
Islam and the Caliphate of Islam and the Caliphate, the ancient Chinese and Turkish adversaries in the struggle against Iran; caused them to play galabe.
Northern Islam, that is, Hanafism, systematized by Abu Hanefi, one of the Khorasan Turks, constitutes 56% of Islam. Reason and Faith support each other. Sufi beliefs abolished the sectarian discrimination, Bektashism formed the infrastructure of the Ottoman expansion in Europe.
Major Axes
- a significant Muslim Turkish population in China, Iran, Russia and Europe;
- Buddhist Turkish population in China and Russia
- There are Christian and Jewish Turkish populations in Russia and Eastern Europe.
The Land of the Holy Land
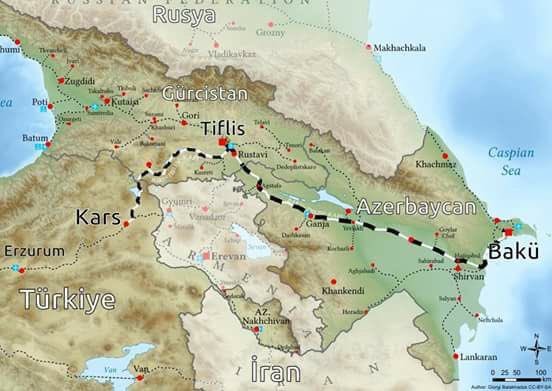
Turkey, the land of the holy land: The Cult of the Mother Goddess Cybele, the House of the Virgin Mary, the Iznik Council, the revival of Orthodoxy in the land of Turkey, 7 holy churches, Hagia Sophia, Mimar Sinan Mosques, Madrasahs, Kulliyes, Prophet Abraham Urfa, Prophet Noah, Noah The Legend of Harran, St. Paul, Antakya, Tarsus, Cappadocia, the first Christians in the Underground Churches, Göbeklitepe (8000 BC), Syriac, Aramaic, Nestorian, Eastern Christianity are all journeys of faith in our country.
Nile – Amudarya (Ceyhun) Nile river and Ceyhun (Amudarya); When two parallel lines are drawn to the east, starting from the points of Alexandria on the Nile and El Luxor Vasit in the south; Alexandria, Memphis, Cairo, Damascus, Jerusalem, Harran (on the periphery) Jerusalem, Nineveh, Baghdad, Babylon, Basra (on the periphery), Uruk (on the periphery), Isfahan (on the periphery), Nishapur, Bukhara, Samarkand.
The Turks existed in the intercontinental cultural contacts that took place on the Nile-Amu Derya/Ceyhun axis, starting from the east from the tip of Samarkand and traveling to the west.
Main Station: Transoxiana Yellow River (Huang Ho) – Ceyhun or Orhun river – The distance between Ceyhun and Ceyhun – Nile are equal. The Turks made their journey to the West, which lasted for centuries, with the intermediate station Transoxiana (Ceyhun-Seyhun).
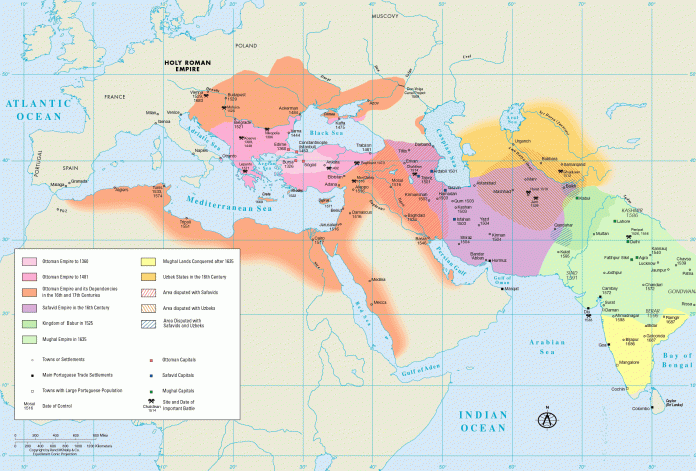
Axis of Hanafism In the early ages of Islam in the 700s, the wise Imam-i Azam Abu Hanifa from Khorasan, patient and realistic in the systematization of Islam, taking steps that combine faith with reason, and in the future, the largest sect of Islam from the Balkans to India, to Bangladesh; A unity of faith and heart has been created that will extend from Tatarstan to Egypt.
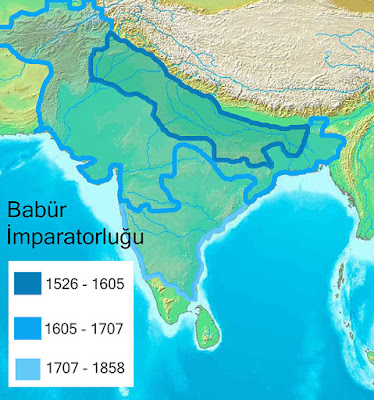
In India , from geographies other than Turkey and Turkistan, the Turkish Mughal Empire in India raised Islam to a rich civilization level in the subcontinent, and enlivened the city of Agra by the Yamuna river with the Taj Mahal. During the Ottoman period, Indian Lodges continued to exist in Istanbul.
Celestial Religions in the Ottoman Empire The Ottomans undertook the representation of all the monotheistic religions; He represented Islam with the Caliphate, Orthodoxy with the Istanbul Patriarchate, Judaism with the Chief Rabbinate, and Armenia with the Patriarchate.
Christianity has its roots in Palestine and Anatolia.
The origin of the Armenian, Syriac and Greek Orthodox churches and beliefs of Eastern Christianity is in the lands of Turkey.
It is Ottoman diplomacy that revealed Protestantism.
Catholic Croats, Armenians, Albanians, Poles, Hungarians, Greeks had positive relations with the Ottoman Empire. The Ottoman lands became the center of the independence struggles of Poland and Hungary.
Transoxiana/Turkestan Renaissance
Between 700-1200 700-1200 Transoxiana centered Turkestan geography renaissance started to live 600 years before Europe. Ulugh Turkestans were familiar with languages and religions. Turkistanis, who were acquainted with the religions and languages of Zoroastrianism, Manicheism, Buddhism, Nestorianism, Syriacism, Hinduism, Islam and Judaism, developed the line of Sufism from all this religious diversity and richness.
Karakhanids and Seljuks (Nizamülmülk, Nizamiye Madrasahs) brought the institution of Madrasa to Islamic Civilization.
In the climate of cultural expanse and interaction that spread from Transoxiana to Iran, to Khorasan, while Turks were publishing the codes of practice of Islam with Nizamülmülk and Gazzali, the Horasan Erens, like Hacı Bektaş-ı Veli, who emerged in the same geography, developed Sufism in a way that would be unique to the Turks.
Turkistan/Horasan – Andalusia Synthesis After
Turkistan/Horasan Sufism, leaping to Anatolia and Rumelia, in addition to Demir Baba/Yellow Saltuk/Yunus/Mevlana/Hacı Bektaş line, the struggle against Ibn Arabi, who migrated from Andalusia, will also take on an identity, the colonizer Dervishes will conquer both continents. They will liven together with dervish lodges, zawiyas and dervish lodges, and they will experience the unity of being both an entrepreneur and a thinker.
Continuous Civilization Line: MMM and the Genetics of Turks
Transoxiana, Mesopotamia and Menderes rivers; From the Nile to the Danube… From the Nile to Ceyhun, from Ceyhun to the Yamuna river; The rich cultural accumulation created by the alluvial soils of the geographies has been ingrained in the genetics of the Turks.
Anatolia, the refuge of believers; It has always been a land of mercy and emigration. Anatolia, which embraced the believers with the underground churches of Cappadocia, embraced the Andalusian Jews in 1492 and the Muslim immigrants exiled from the Balkans and the Caucasus in the 1800s.
Mimar Sinan, who prospered the Ottoman realms with 375 architectural works, including 81 mosques; He is an Anatolian believer and genius who adorned the geographies and lands of the Islamic Civilization with lights.
The Taj Mahal Tomb built by the Mughal Turkish Empire to represent the Islamic Civilization on the banks of the Yamuna river in India, and the Selimiye Mosque built by Mimar Sinan during the Ottoman Empire around the Meriç River in Edirne; They compete with each other in the UNESCO World Heritage List.
Mosques of Samarkand, Bukhara, Kashgar; Istanbul’s Selatin Mosques, Hagia Sophia Church/Mosque, Caspian Synagogues, Rumeli Lodges are the clear manifestations of the Perfection in the Civilization Journeys of the Turks who have expressed their identities in various faiths.
To the City: Life and Death Along the Ancient Walls of Istanbul
$1.92 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Turkish Urban Dictionary: 500 Slang Words & Phrases to Speak Like a Local in Turkey (Urban Slang Dictionary)
$17.90 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Istanbul For First Timers: A Local's Travel Guide To Turkiye's Hidden Gems and Culture
$15.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)The Turkish Cookbook
$40.01 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)The Mini Rough Guide to Istanbul and the Aegean Coast: Travel Guide with eBook
$9.70 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)The History of Istanbul: From Byzantion to Modern Times (History of Turkey Books)
$15.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Lonely Planet Pocket Istanbul (Pocket Guide)
$11.38 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Rick Steves Istanbul: With Ephesus & Cappadocia
$15.21 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Istanbul Travel Guide 2025: Discover Istanbul’s Top Attractions, Hidden Gems, Cultural Highlights, Timely Itineraries, and Budget-Friendly Hacks for Every Traveler
$0.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Rick Steves Istanbul: With Ephesus & Cappadocia
$3.38 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Fodor's Essential Turkey (Full-color Travel Guide)
$3.38 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Time Out Istanbul
$2.20 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Ancient Turkey: A Traveller's History
$7.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Colors of Asia: A Visual Journey
$34.00 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Lonely Planet Pocket Istanbul (Pocket Guide)
$11.38 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Conversational Turkish Dialogues: Over 100 Turkish Conversations and Short Stories (Conversational Turkish Dual Language Books)
$6.40 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Rick Steves Istanbul: With Ephesus & Cappadocia
$15.21 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Istanbul, City map 1:10.000, City Pocket map + The Big Five
$11.92 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Istanbul For First Timers: A Local's Travel Guide To Turkiye's Hidden Gems and Culture
$15.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)The Amazing Mrs. Pollifax (Mrs. Pollifax Series Book 2)
$5.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Iron Silk Road opens… Train from London will be able to go as far as Beijing
Rick Steves Istanbul: With Ephesus & Cappadocia
$15.21 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Istanbul Travel Guide 2026: Top Places to Visit, Things to Do, Exploring Neighborhood, Itineraries, Festivals and Events, Food and Drink, Shopping, ... History And Culture. (EXPLORE THE GLOBE)
$13.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Rick Steves Istanbul: With Ephesus & Cappadocia
$3.38 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)The Turkish Cookbook
$40.01 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Modern Istanbul Map / Modern Istanbul Haritasi: Guide to Modern Architecture in Istanbul, Turkey (Blue Crow Media Architecture Maps)
$13.00 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Istanbul Travel Guide 2026: Your All-in-One Resource: Explore Must-See Attractions, Curated Itineraries, Budget-Friendly and Accessible Stays, Up-to-Date Essentials, and Sustainable Travel Tips
$15.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Wonders of Istanbul: A Photo Collection of the City’s Most Beautiful Places to See – A Stunning Coffee Table Travel Photobook
$23.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)The History of Istanbul: From Byzantion to Modern Times (History of Turkey Books)
$15.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Istanbul & Northwest Turkey Travel Reference Map WP
$9.89 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)DK Top 10 Istanbul (Pocket Travel Guide)
$11.39 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)DK Eyewitness Travel Guide: Turkey
$4.46 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)High Albania
$0.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Istanbul, City map 1:10.000, City Pocket map + The Big Five
$11.92 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Istanbul: Memories and the City (Vintage International)
$5.68 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)DK Top 10 Istanbul (Pocket Travel Guide)
$2.68 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Lonely Planet Pocket Istanbul (Pocket Guide)
$11.38 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Making Out in Turkish: Turkish Phrasebook (Making Out Books)
$6.12 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)The Amazing Mrs. Pollifax (Mrs. Pollifax Series Book 2)
$5.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)The Turkish Cookbook
$40.01 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)A Guide to Biblical Sites in Greece and Turkey
$15.71 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Cyprus is the center of the world
In their own interests the 19th and 20th centuries, Central Asia , the Middle East created the concept Despite the western Atlantic powers, the ancient thousands of years that until the old-time reality Mediterrane (Mediterranean) and Zhongguo (China), the meaning of those so-called Middle Earth ‘is.
The Center of the World, the rare island of the Mediterranean, Cyprus, with its location holding the center of the Cradle of Civilizations, has a global potential as a treasure of ideas of the Basin.
The comparative advantage of Cyprus is its location and opportunity as an island of ideas, a paradise for contemplation, and a center for the production of high-value ideas.
It is extremely important that European philosophy from the continents surrounding the Mediterranean cannot be grasped without the developmental process that took place elsewhere and passed to Europe. The beginnings of the development of Western philosophy lie in the region that the Hellenes called the Orient (Anatole). The first center here was Miletos. Thales, Anaximandros and Anaximenes became the first philosophers of the history of philosophy with their intellectual activity and the problems they addressed.
The second and main center was in Europe: Athens. However, the third center right after that, Alexandria (Alexandria), is again outside the borders of Europe in Egypt, and the next one, Baghdad, is a little deeper in the Orient. Source: Elmar Holenstein, Atlas of Philosophy, Spaces and Ways of Thinking, June 2015, Istanbul, Küre Publications
Cyprus, located in the middle of the Miletus-Alexandria-Baghdad triangle; It is in a position to reproduce the Minor Asia-Greater Asia-Africa intellectual heritage.
Cyprus has started to accumulate an important intellectual infrastructure for years by providing education to the students of the countries in the triangle in question at the universities on the island. Starting from the coming years, targeting the world’s first place in intellectual activities of this accumulation should be put on the agenda.
Our knowledge shows that the mental conditions for philosophizing began in Africa. The most important contribution of the African continent to philosophy is the ability to speak. Having the ability to speak means that a person has the cognitive ability to not only understand but also reveal every philosophy that has developed since the Axial Age 2500 years ago. Early humans, who spread from Africa to the whole world between 50,000 and 100,000 years ago, carried this ability with them. Source: Elmar Holenstein, Atlas of Philosophy, Spaces and Ways of Thinking, June 2015
Cyprus, where Time and Grounds intersect, will bring out a universal Mind from the treasure of these intersections and will make it available to all humanity.
Despite the European Hegenomy, which only achieved dominance for 500 years by using external resources that did not belong to it; Mathematics and rationality of Asia Minor, symbolized by Miletus; Diophantus mathematics symbolized by Alexandria, Pythagorean wisdom (sophia) and Harezmi mathematics symbolized by Baghdad, wisdom of Beytül Hikme; In the Center of the World, Cyprus, the Afrasia Millennium, which has emerged from its own resources since the beginning of the 21st century, is preparing to take its place in history as the 3rd Millennium. The richness of thought of Ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia and Transoxiana is being reshaped on the island of Cyprus.
All innovations (paper, printing press, gunpowder, compass) to Europe were carried from Greater Asia by the Silk Road and the Iron Silk Road, which will be operational from 2035, will connect the New Mediterranean (Pacific Ocean) with the Cyprus-based Mediterranean. While Asia Minor Turkey was woven with iron nets in 1935s, a century later, 2035s will be the beginning of a new era, the Silk Road Age, in which Greater Asia will connect the oceans with railways.
In the early ages, the ancient Greek civilization emerged from the Mediterranean Civilization, which was common among the nations living on the Mediterranean coast, which was formed with the help of the Egyptians, Sumerians, Hittites, Assyrians and Phoenicians, and the ancient Roman civilization from the Greek civilization. After it was divided into two as Eastern Rome and Western Rome, the Europeans, who were the heirs of Western Rome, adopted this civilization and advanced it. Source: Ziya Gökalp, Principles of Turkism, Ministry of National Education Press, 1st Edition. Istanbul 1976, p. 48. 132 Ibid. NS. 136
Eastern Rome, on the other hand, was continued as the Seljuk and then the Ottoman Empires by the Turks, who stretched from Far Asia to Asia Minor, with the victories of 1071 and 1453. Thus, the Mediterranean Civilization, as a unique civilization with many components, has thousands of years of history and dynamic interactions.
Skopje (Macedonia), where Turkish culture is extremely strong as in Cyprus, is the birthplace of Yahya Kemal Beyatlı, one of the greatest poets and intellectuals of Turkish poetry. Yahya Kemal, who sees his geography within the Mediterranean civilization basin, strives to reach the universal, especially through this thesis. He realistically determined the borders (misak-ı milli) and then the milestone (1071 and 1453) of the homeland, from which he claimed to have been created as an indivisible whole by the religion and the nation, and included it in the European civilization through the Mediterranean basin with a final effort. Of course, while establishing this synthesis, he takes care not to overlap with any doctrine, theory, and not to construct theories that will impose responsibility on himself.“The homeland is never a theory, it is a land. Soil is the tomb of the ancestors. It is where mosques are built. Industry is the exhibition of what has been done in the name of nafise (Fine Arts).” Source: Kadrican Mendi, Yahya Kemal’s Politics
“The reflection of Yahya Kemal; It is on the line of Vienna, Budin, Belgrade, Istanbul, Baghdad, Basra. Yahya Kemal Bey’s reflective side is also important; It has prose style writings.” Source: Ömer Tuğrul İnanç
Time Out Istanbul
$2.20 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Istanbul, City map 1:10.000, City Pocket map + The Big Five
$11.92 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)The History of Istanbul: From Byzantion to Modern Times (History of Turkey Books)
$15.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Istanbul Travel Guide 2025/2026: Sultanahmet, Beyoğlu: Shopping and Nightlife, Kadıköy, Balat and Fener, Markets and Shopping,Hagia Sophia,Must-See ... Galata Tower. (Best Travel Guides 2025)
$11.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Istanbul Travel Guide 2026: Your All-in-One Resource: Explore Must-See Attractions, Curated Itineraries, Budget-Friendly and Accessible Stays, Up-to-Date Essentials, and Sustainable Travel Tips
$15.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Rick Steves Istanbul: With Ephesus & Cappadocia
$3.38 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Modern Istanbul Map / Modern Istanbul Haritasi: Guide to Modern Architecture in Istanbul, Turkey (Blue Crow Media Architecture Maps)
$13.00 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Lonely Planet Istanbul (Travel Guide)
$5.49 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Blue Guide Istanbul
$9.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Laminated Istanbul Map by Borch (English) (English, Spanish, French, Italian and German Edition)
$5.96 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Lonely Planet Turkiye (Travel Guide)
$12.77 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Ancient Turkey: A Traveller's History
$7.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Colors of Asia: A Visual Journey
$34.00 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Istanbul For First Timers: A Local's Travel Guide To Turkiye's Hidden Gems and Culture
$15.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)The Turkish Cookbook
$40.01 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)The Christian Traveler's Guide to the Holy Land
$9.97 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)DK Top 10 Istanbul (Pocket Travel Guide)
$2.68 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Istanbul, City map 1:10.000, City Pocket map + The Big Five
$11.92 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Fodor's Essential Turkey (Full-color Travel Guide)
$16.60 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)The Amazing Mrs. Pollifax (Mrs. Pollifax Series Book 2)
$5.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)The Middle East: From Empires to Fragmentation
Western structures such as the United Kingdom, the United States, the European Union; They have no tolerance for union formations other than themselves.
The Turks prevented the Chinese from descending into the Middle East with the Talas War (740) and the Byzantines with the Seljuk expansion (1000s). Thus, the two imperial empires were prevented from descending to the center of the world.
UNITY
-
Turkish/Arab (Talas, 741): China was prevented from landing in the Middle East. Instead, the Turks landed in the Middle East.
-
Turkish/Arab/Kurdish: Fatih, Akşemsettin, Molla Gürani, Istanbul was conquered. (1453)
-
Turkish/Kurdish: Caliphate and conquest of Egypt. Yavuz Sultan Selim (1517)
-
Turkish/Kurdish/Armenian: Conquest of Anatolia (1071)
-
Turkish/Kurdish: War of Independence. Eastern Anatolia (1919)
-
Turkish/Greek: Fatih/Patriarch Gennadios, Dimitri Kitsikis, Turkish-Greek empire: A look at Ottoman history in the light of the reality of the intermediate region
Middle Eastern Empires:
-
Kingdom of Egypt, 1450 BC
-
Hittite Empire; 1340 BC
-
the Kingdom of Israel; 1050 BC
-
Assyrian Empire, 721 BC
-
Babylonian Empire; 600 BC
-
Persian Empire; 550 BC
-
Macedonian Empire; 336 BC
-
Roman Empire ; 44 BC
-
The Byzantine Empire; AD 565
-
Sassanid Empire; AD 610
-
Umayyad Empire; AD 750
-
Seljuk Empire ; 1100 AD
-
Crusader Kingdom; AD 1140
-
Saladin’s Ayyubid Empire; AD 1187
-
Mongol Empire; AD 1279
-
Ottoman Empire ; AD 1700
-
Independent States: AD 1971
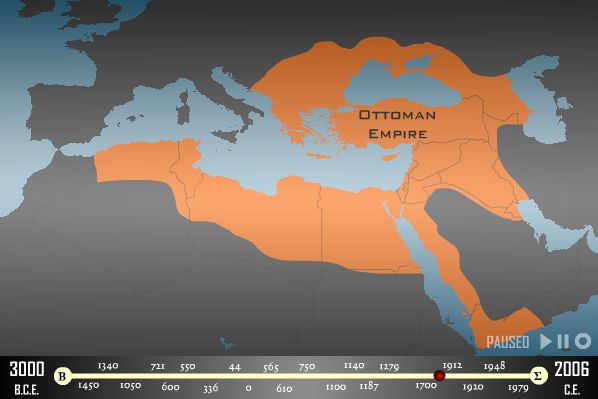
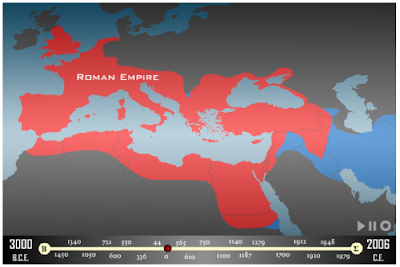
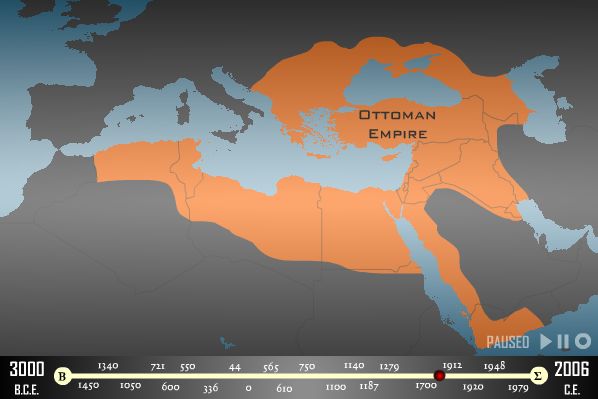
In the Age of Empires, which started with the Kingdom of Egypt in 1450 BC and ended with the Ottoman Empire in 1920;
– A total of 16 Empires
– 15 of these empires, excluding the Kingdom of Israel, are related to the territory of Turkey.
– North (Turkey) centered empires: Hittite, Byzantine, Seljuk, Ottoman: 4
– South centered empires: 7
– East centered empires: 3
– West centered empires: 2
Total: 16
Although the centers of the Empires in the South, East and West directions are scattered, all 4 Empires in the North direction are centered in TURKEY.
ANATOLIA, starting from HİTİT in 1350 BC; It has become the control-command center of the Middle East.
Two of these empires were the TURKISH EMPIRE; Seljuk and Ottoman.
In no other part of the world have layer-by-layer empires overlapped and wealth accumulated in this way.
The Ottoman Empire had the accumulation of 15 Middle Eastern Empires behind it, and the West, which decided to end this huge wealth and accumulation, achieved its goal in October 1918.
Among the Middle Eastern Empires, the Ottoman Empire reached a record for 620 years, the region was torn apart by its destruction, and as a result, there was a century-long war, chaos and massacres.
The unjust hegemony of the West has turned the region into a bloodbath.
Fragmentation of the Middle East Union:
-
1922 Egypt
-
1923 Turkey
-
1925 Iran
-
1932 Arabia
-
1932 Iraq
-
1946 Jordan
-
1946 Syria
-
1946 Lebanon
-
1948 Israel
-
1951 Libya
-
1956 Morocco
-
1956 Sudan
-
1956 Tunisia
-
1961 Kuwait
-
1962 Algeria
-
1967 Yemen
-
1970 Oman
-
1971 UAE
-
1971 Bahrain
-
1971 Qatar
1450 BC
KINGDOM OF EGYPT
1340 BC
HIITITE EMPIRE
1050 BC
KINGDOM OF ISRAEL
600 BC
Babylonian Empire
550 BC
PERSIAN EMPIRE
336 BC
EMPIRE OF MACEDONIA
44 BC
ROMAN EMPIRE
AD 565
THE BYZANTINE EMPIRE
AD 610
SASANI EMPIRE
AD 750
Umayyad Caliphate
1100 AD
SELJUK EMPIRE
AD 1140
THE KINGDOM OF THE CROSSES
AD 1187
SELAHATTIN EYYUBI EMPIRE
AD 1279
MONGOLIAN EMPIRE
AD 1700
OTTOMAN EMPIRE
AD 1971
INDEPENDENT STATES
Middle East
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DHJLzP8q790
By Bilge Tonyukuk Institute at September 02, 2015
Stamboul Ghosts: A Stroll Through Bohemian Istanbul
$20.02 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Pocket Rough Guide Istanbul: Travel Guide with eBook
$9.40 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Laminated Istanbul Map by Borch (English) (English, Spanish, French, Italian and German Edition)
$5.96 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Istanbul Travel Guide 2025/2026: Sultanahmet, Beyoğlu: Shopping and Nightlife, Kadıköy, Balat and Fener, Markets and Shopping,Hagia Sophia,Must-See ... Galata Tower. (Best Travel Guides 2025)
$11.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)DK Eyewitness Travel Guide Istanbul (Eyewitness Travel Guides)
$10.26 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)DK Eyewitness Istanbul (Travel Guide)
$9.65 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Rick Steves Istanbul: With Ephesus & Cappadocia
$15.21 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Istanbul For First Timers: A Local's Travel Guide To Turkiye's Hidden Gems and Culture
$15.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)The Mini Rough Guide to Istanbul and the Aegean Coast: Travel Guide with eBook
$9.70 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Rick Steves Istanbul: With Ephesus & Cappadocia
$3.38 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)DK Top 10 Istanbul (Pocket Travel Guide)
$11.39 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Ancient Turkey: A Traveller's History
$7.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Fodor's Essential Turkey (Full-color Travel Guide)
$16.60 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)DK Eyewitness Travel Guide: Turkey
$4.46 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Fodor's Essential Turkey (Full-color Travel Guide)
$3.38 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Istanbul: City of Majesty at the Crossroads of the World
$4.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Lonely Planet Pocket Istanbul (Pocket Guide)
$11.38 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)DK Top 10 Istanbul (Pocket Travel Guide)
$2.68 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)The Christian Traveler's Guide to the Holy Land
$9.97 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Making Out in Turkish: Turkish Phrasebook (Making Out Books)
$6.12 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Asian Travellers of Turks
- India Through Biruni’s Eyes
- saint-celebi
- Five Turks in Asia
- east-asiyaya-travel-amp-asiyayi-sarkiye-travel
- istanbul-to-asiyayi-vustaya-travel
- Halide Edip Adıvar, About India
- Emel Esin, Turkistan Travel Book
- Niyazi Berkes: Letters from Asia
- Ergun Çağatay -once-central-asia
- Servet Somuncuoglu
- Kursat Yildirim
- Ilber Ortayli

Istanbul Travel Guide 2025: Discover Istanbul’s Top Attractions, Hidden Gems, Cultural Highlights, Timely Itineraries, and Budget-Friendly Hacks for Every Traveler
$0.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Wonders of Istanbul: A Photo Collection of the City’s Most Beautiful Places to See – A Stunning Coffee Table Travel Photobook
$23.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)The Mini Rough Guide to Istanbul and the Aegean Coast: Travel Guide with eBook
$9.70 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Modern Istanbul Map / Modern Istanbul Haritasi: Guide to Modern Architecture in Istanbul, Turkey (Blue Crow Media Architecture Maps)
$13.00 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Crescent and Star: Turkey Between Two Worlds
$6.49 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)The Turkish Cookbook
$40.01 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Lonely Planet Istanbul (Travel Guide)
$5.49 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Istanbul For First Timers: A Local's Travel Guide To Turkiye's Hidden Gems and Culture
$15.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)DK Eyewitness Istanbul (Travel Guide)
$9.65 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)DK Top 10 Istanbul (Pocket Travel Guide)
$11.39 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Istanbul: City of Majesty at the Crossroads of the World
$4.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Türkiye (Turkey) Map (National Geographic Adventure Map, 3018)
$11.87 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Lonely Planet Pocket Istanbul (Pocket Guide)
$11.38 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Colors of Asia: A Visual Journey
$34.00 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Ancient Turkey: A Traveller's History
$7.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)DK Eyewitness Travel Guide: Turkey
$4.46 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)The Amazing Mrs. Pollifax (Mrs. Pollifax Series Book 2)
$5.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)The Christian Traveler's Guide to the Holy Land
$9.97 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Istanbul For First Timers: A Local's Travel Guide To Turkiye's Hidden Gems and Culture
$15.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Learn Turkish in 100 Days: The 100% Natural Method to Finally Get Results with Turkish! (For Beginners)
$9.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Turkish Presence in India
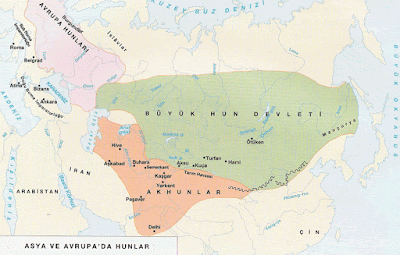
- Kushanlar
- Akhuns, Huns
- ephthalite
- Ghaznavids
- Timur
- Mughal
- The Taj Mahal
- Sindh Province
- Punjab Province
- neighbor with Turkestan
- Khwarezmi
- Turks traveling to India
- Buddhism and Turks
- Yellow Uighurs (Buddhist)
- Burhanism
- mysticism
- Istanbul Indian Lodges
- National struggle
- Gandhi, Nehru
- Khwarezmi (780-850)
- Biruni (d.1048)
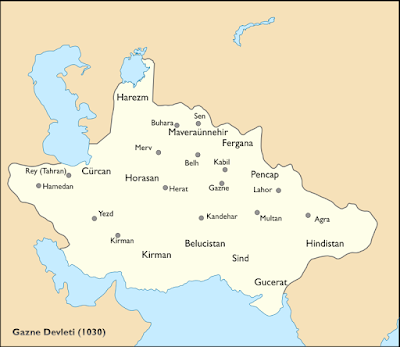
- Al-Hujviri: The source of Punjabi Sufism: Ali Al-Jullabi Al-Hucviri from Gazne, owner of Kashfu’l-Mahjub, namely “Data Genc Bahş.” His tomb is in Lahore
- He was born before Ahmet Yesevi. (d.1049) http://www.islamancyclopedisi.info/dia/pdf/c18/c180267.pdf
- Halide Edip
- Yusuf Hikmet Bayur
- Cemil Meric
- Müfid Yüksel http://mufidyuksel.com/arakanrohang-ve-hint-muslimanligi-1.html https://twitter.com/mufidyuksel/status/663133651119546372 http://www.haber10.com/yazar/haber_10/turkiyede_naksibendilik_etnik_milliyet_ve_medreseler- 39930
- Pakistan Bangladesh
- Haluk Erkmen Indian writings
- Tonybee Oxus to Jamuna
- Agra, Lahore, New Delhi
- The Effects of Turks on Indian Civilization article
- Ottoman Navy in the Indian Ocean
- Model country India
- The first meaning of the term Middle East
- İlber Ortaylı Indology
- Ecevit in Sanskrit
- The Indians who were made to fight against the Ottomans in the wars such as the Dardanelles.
- Mumbai Chronicle
- Ataturk and India
- Caliphate Fund
- Hong Kong Kowloon Mosque built for Muslim Indian soldiers
- Travel book Ortaylı
- Iskender
- History of India: Yusuf Hikmet Bayur
- Expeditions to India from the North: ASAM
- empires
- Our model country: India
- Islam was fragmented in India before the Ottoman Empire.
- Prof Hoffman: India
- cheap innovation
- Oxus: tonybee
- Khorasan and the Turkish world
- Buddhism
- buddhist turks
- Octagon Burhan Lives Coruh
- caste system
- Penjab: Sufism
- indology
- Trademap trade information
- Khorasan and the Turkish world
- Turks in India (100 million)
Northern Islam (Hanafi) line
- Indian subcontinent (in India, Bangladesh and Pakistan),
HALUK BERKMEN
Jiddu Krishnamurti http://www.halukberkmen.net/pdf/222.pdf
Participatory Awareness http://www.halukberkmen.net/pdf/256.pdf Knowing
Yourself http://www.halukberkmen.net/pdf/189. pdf
Age of Giants http://www.halukberkmen.net/pdf/267.pdf
Lost Continent MU http://www.halukberkmen.net/pdf/227.pdf
Development of Literature http://www.halukberkmen.net/pdf/ 51.pdf
“ URDU is spoken in the north-west of India and Pakistan. This language is close to the language of the Asian Turks who came from the north. It is originally an ORDU language and has been mixed with Persian and Hindi over time. Place names may also have changed. Because Indian culture is unique and has adapted the names to their own pronunciation.” Haluk Berkmen
HAND HAREZMI
India first started counting numeral expressions 300 years ago. Toward the 6th century, numbers 1 through 9 appeared, with digits from right to left. These figures began to be recognized outside of India around 660.
Kitab al-Muhtasar fil Hisab al-Hind.
EL BIRUNI
1017 from Gazneli Mahmut , Khwarezm State ‘s destruction by Biruni in Ghazni came to the city where Gazneliler ‘ s auspices entered. He was highly respected in the palace and joined Mahmud of Gazne’s expedition to India . Here he attracted the attention of Indian scientists, and when the Indian country was conquered , he settled in the city of Nendene and continued his scientific studies here. He studied the life and culture of Indian society by learning Sanskrit .
It is understood from his letters that Bîrûnî knew Aristotle . Working with important scholars such as Ibn Sînâ , Birûnî went to India many times. That’s why he wrote a book on India. This book of his has been translated into several languages. This book, which has been translated into several languages, has set an example for many scholars. Birûni also has one novel.
Kitâb’üt-Tahkîk Mâ li’l-Hind: Bîrûnî, who also wrote a book on Indian history, described the superstitions, beliefs, lifestyles and customs and traditions that the Indians believed in in great detail, and while doing this, he acted completely impartially and away from prejudices.
——————————————-
Indian travel books have a special place in our literature. Al-Biruni’s Indian Travel Book is the work accepted even by the eminent scholar Hindus, who became eternal in the history of the East, and that even Nehru lauded. Al-Biruni, who is fluent in Persian and Arabic, even learned Sanskrit for India. The information he gave aside; He is the man who uses some of the knowledge that remains within the borders of this country and transfers his science to the Eastern world. (Medium)
—————————————––
Walter Ruben (hindologist)
As in the whole of his intellectual adventure, he sometimes complains about not being able to find his reader and not being understood during this sensitive work. But this world, where he invites everyone, is the homeland of freedom of thought. “Indian”, says Meriç, “because it is a country that gives a voice to every faith, it has become my second homeland. In this book there is the whole Indian with his dreams and his reality… that is, the whole human being.”
 a
a“The book written by a Turkish intellectual, Halide Edip, on India in the 1930s; in other words, “Inside India” had a great impact in its time. This book about the necessity of Muslim India is still discussed and is a well-known classic. Halide Hanım stayed long in India. He gave lectures at institutions such as Aligarh Islamic College. He made friends with all the great Indian intellectuals of the time. The report he wrote is considered one of the main works that point to the future of the country.” http://www.
HINDOLOGY, İlber Ortaylı
http://leventagaoglu.blogspot.com.tr/2016/02/tefekkur-medeniyet-hindoloji-z-ilber.html
Turkish Travel Books on India from the 19th Century to Our Time http://dergiler.ankara.edu.tr/dergiler/42/457/5210.pdf
The Effect of Turkish Culture on Indian Civilization
http://tdid.ege.edu.tr/files/dergi_12/22.pdf
Expeditions to India from the North
My India in 23 items
09.01.2016Ayşe Arman @ Hürriyet (650+)
The exemplary journey of India and Pakistan
29.12.2015Cemal Tunçdemir @ T24 (100+)
indian boy
18.01.2016Yonca Tokbaş @ Hürriyet (40+)
in Ottoman India
29.12.2015Ali Sirmen @ Cumhuriyet (30+)
Why shouldn’t India be our new market?
09.02.2016Güntay Şimşek @ Habertürk (5)
He brought Batman and Superman together on a croissant and settled in India
07.12.2015Vahap Munyar @ Hürriyet (10+)
“The Conqueror of India” Mahmud of Ghazna
Search: INDIA
14 article(s) matched your criteria.
- The Russian Occupation of Eastern Anatolia in the Ottoman-Russian War of 1828-1829 and Its Effect on the British Road to India Policy / Uğur Akbulut [The Caucasus Special Issue- III; 703] For other articles in this volume, click here.
- India of the Turks / Enver KONUKÇU [Turkish World I; 355]Click for other articles in this volume.
- XV. Ottoman Traders in India at the End of the Century / Prof. Dr. Halil SAHİLLİOĞLU [3/77]Click for other articles in this volume.
- First Turkish Domination in India: Kushans and Akhuns / Prof. Dr. Salim Cöhce [1/815-820]Click for other articles in this volume.
- Dominion of Ghaznavids in India / Prof. Dr. Salim Cöhce [4/522-525]Click for other articles in this volume.
- Turkish States Established in India / Prof. Dr. Salim Cöhce [8/689-730]Click for other articles in this volume.
- Mughals: “The Temürs in India” / Prof. Dr. Enver Konukçu [8/744-760]Click for other articles in this volume.
- Turkish-Muslim Architecture and Art in India / Prof. Dr. İnci Macun [8/881-890]Click for other articles in this volume.
- Architecture and Art of Timurids in India / Prof. Laura Parody [8/891-899]Click for other articles in this volume.
- Sultan II. Ottomans and Indian Muslims in the Period of Abdulhamid / Assoc. Dr. Azmi Özcan [13/138-143]Click for other articles in this volume.
- First Turkish Domination in India: Kushans and Akhuns / Prof. Dr. Salim Cöhce [1/569-579]Click for other articles in this volume.
- Turkish States Established in India / Prof. Dr. Salim Cöhce [5/313-385]Click for other articles in this volume.
- Mughals: “The Temürs in India” / Prof. Dr. Enver Konukçu [5/387-414]Click for other articles in this volume.
- Turkish-Muslim Architecture and Painting in India / Prof. Dr. İnci Macun [5/447-460]Click for other articles in this volume.
SEARCH: INDIA
- Turkish States in India / Prof. Dr. Salim Cöhce [2/925-941]Click for other articles in this volume.
- Baburids: Timurids in India / Prof. Dr. Enver Konukçu [2/942-959]Click for other articles in this volume.
- Turkish Islamic Architecture and the Art of Painting in India / Prof. Dr. İnci Macun [2/998-1000]Click for other articles in this volume.
- Architecture and Arts of the Indian Timurids / Dr. Laura Parody [2/1008-1015]Click for other articles in this volume.
- The Ottomans and Muslims of India during the Reign of Sultan Abdulhamid II / Assoc.Prof. Dr. Azmi Özcan [4/299-303]Click for other articles in this volume.
Agra – Mughal Shah
Zahiriddin Muhammed Babur –
Rick Steves Istanbul: With Ephesus & Cappadocia
$3.38 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Modern Istanbul Map / Modern Istanbul Haritasi: Guide to Modern Architecture in Istanbul, Turkey (Blue Crow Media Architecture Maps)
$13.00 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Istanbul: Memories and the City (The Illustrated Edition)
$11.93 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Stamboul Ghosts: A Stroll Through Bohemian Istanbul
$20.02 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Lonely Planet Pocket Istanbul (Pocket Guide)
$11.38 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Pocket Rough Guide Istanbul: Travel Guide with eBook
$9.40 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Turkish Urban Dictionary: 500 Slang Words & Phrases to Speak Like a Local in Turkey (Urban Slang Dictionary)
$17.90 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Laminated Istanbul Map by Borch (English) (English, Spanish, French, Italian and German Edition)
$5.96 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)The Turkish Cookbook
$40.01 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Crescent and Star: Turkey Between Two Worlds
$6.49 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Fodor's Essential Turkey (Full-color Travel Guide)
$3.38 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)The Christian Traveler's Guide to the Holy Land
$9.97 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Istanbul, City map 1:10.000, City Pocket map + The Big Five
$11.92 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Crescent and Star: Turkey Between Two Worlds
$6.49 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Ancient Turkey: A Traveller's History
$7.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)High Albania
$0.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)A Guide to Biblical Sites in Greece and Turkey
$15.71 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Turkey Travel Guide: Captivating Adventures through Rich History, Turkish Delights, Turkish Landmarks, Hidden Gems, and More (Traveling the World)
$13.69 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Collins Turkish Phrasebook and Dictionary Gem Edition (Collins Gem)
$0.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Learn Turkish in 100 Days: The 100% Natural Method to Finally Get Results with Turkish! (For Beginners)
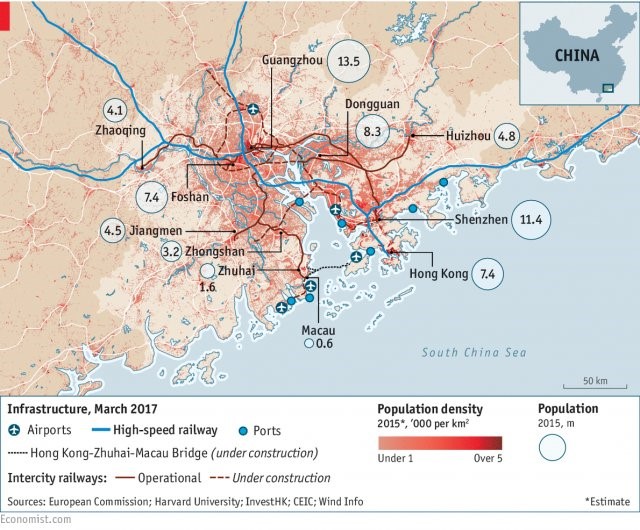
$9.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Thrace region Turkey and Canton province China in comparison
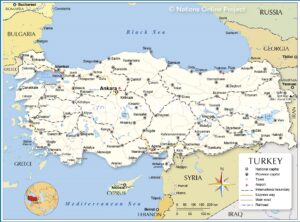
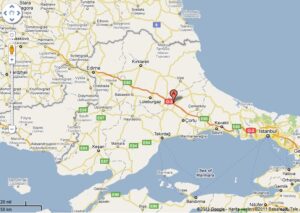
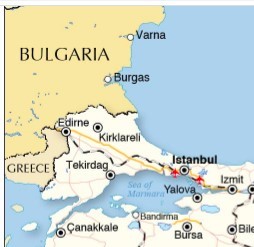
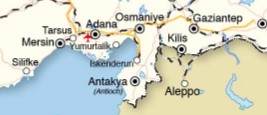
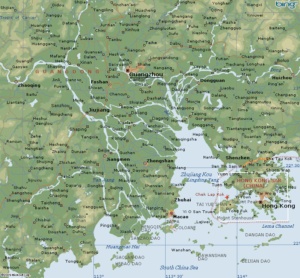
Within Turkey inside, there are two regions which look like to Canton province of China.
First is Thrace region connecting Turkey to go to Europe so this is this is mainly plane plane ticket today and there is the transfer European motorbike TEM connecting connecting took you to your destinations so in the end and interest rates and there are alsoBut I also text Aylılıç and say leather factories and then all kinds of light industrial productions that Europe is demanding the products so the shipments bye-bye truck is very speedy say through Çay through Bulgaria Romania hungry then you press to Austria and Germany were directly so sorry also more than 50% of turkey experts are destined to do European union this is very important fact so unlike China turkey is more connected to You are up north to the US UK and Germany Italy and France they are the top export markets for 30 bucks turkey turkey.
And further the second reason is it looking like Canton promise is in insults insults this isIn eastern Mediterranean region the port city of Maxine Main container experts porch for containers to China to Asia may need to you’re a boy is well and then Maxine is in connection very close to Atlanta city which is very like Canton it is very humid and hot city but it is the area of cotton so or not it is Montana’s however there are two Rivers inside and it is very industrial base with İn and Ava culture of the base is well the other night city and text other city is it so amazing I don’t know I’m Gracian tip line is very dynamic their dynamic activity area for the containers for the shipments did the goods produced in in case Siri what is cities and Kahraman cities as well I’m in insight Center alone I told you I’m done I’m Tyler regionAntalya region is getting close to Maxim and the production and other city all shipments all good collect it from these from the factories and from the pills in the cities are distance for export so so finally we may conclude that for the road transport to Europe 30 surgeon is very basic and Turkey connecting turkey to Europe and secondly do it in the south eastern Mediterranean region around Mac’s in Port cityThese are destined for shipments all over the world to Europe to Asia to Africa you say to Africa is very close as well Maxine city to North Africa cities in Libya Tunisia and Algeria they are very very close also Italy France Spain and they are very close also from Maxim and to the passing through the Swiss canal channel so the shipments are the best thing for Asia Pacific markets not.
Investment Case: Soda Ash by China
No technology and investment is very important in Turkey’s products is one of the top 10 items in the world and China Inn introduced credit line and a technology for the establishment of factories factories in one in Kazan town and the other is in by Pass liquor town in capital city on Krieg countryside so this is natural mine so now million is has the capacity for sodas for turkey and this is even evenEven shipped it to China this is very crucial for the world market and so that is introduced in textiles in in detergent in mining in food in variety of industries so you switch is very diversified diversified so this is good for the market coverage and penetration and distribution.
Turkey: South Eastern Europe Country
Turkey is so soft is it eastern Europe country and it is similar to in this respect to South East Asia because also answer key is also surrounded by buy the season like South East Asia like south east Asia has connections with many parts in Asia Pacific Lykos Australia Japan Korea ChinaAnd turkey also has direct flights relations with the European Union with Middle East with Russia Iran and Africa eastern Mediterranean countries you see many regions so chunky is like a horse in the in the legends entering into into Europe Asia and Africa continent three continents mainly so maybe I’ll read all these aspects fromFrom the market penetration view and understanding.
I am against similar point is that China has historical ties in south Asia and south east Asian countries say in Indonesia Malaysia Philippines Vietnam Cambodia Laos China community is there who hold economic power and power in these countries are there is a Chinese corn inside these markets and states and in the same way (tercüme) also has hisHistorical and cultural ties ties say in the south east Europe in bulk and say Romania Moldova then ask Yugoslavia countries like Grassia Montenegro Bosnia Slovenia Kosova as well and bless plus hungry and Slovakia and in Eastern Europe again this historical ties are valid say in Poland Lithuania Latvia Lithuania and includingSweden on top so these Eastern Europe and south eastern Europe countries has definitely been a strong ties and this is and this is also our village inn in North Africa like Algeria miracle Tunisia Egypt and then in in Sudan as well plus in the Middle East in Iran Syria Iraq Lebanon and Israel Jordan Palestine and Saudi ArabiaAnd the golf camp for them plus connections stands because I stand stand stand stand Afghanistan Mongolia all these connections ties with China is the sensor for the eastern Asian turkey is the Center for West end south east Europe and then the other regions around five C’s say Lexi Mediterranean right see Caspian Sea and then golf so golf so.
So the cooperation between China and is mainly based on silk Road Road where to be connected to the sub regions all by China site and cite the sub regional centers for business development and industrial development development may happen in all these wide areas and more is tax and Chinese the ties and then they know each other very well they are not they are not for foreigners for themselves they have their knowledgeBy BYOYO bilateral.
Istanbul For First Timers: A Local's Travel Guide To Turkiye's Hidden Gems and Culture
$15.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Istanbul Travel Guide 2026: Your All-in-One Resource: Explore Must-See Attractions, Curated Itineraries, Budget-Friendly and Accessible Stays, Up-to-Date Essentials, and Sustainable Travel Tips
$15.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Stamboul Ghosts: A Stroll Through Bohemian Istanbul
$20.02 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Laminated Istanbul Map by Borch (English) (English, Spanish, French, Italian and German Edition)
$5.96 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)The History of Istanbul: From Byzantion to Modern Times (History of Turkey Books)
$15.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Rick Steves Istanbul: With Ephesus & Cappadocia
$15.21 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)TURKEY TRAVEL GUIDE 2026-2027: Discover Istanbul, Cappadocia, Ephesus, Pamukhale & Antalya: Local Secrets, Expert Tips, Hidden Gems, Cultural Insights, and Smart Itineraries
$5.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Pocket Rough Guide Istanbul: Travel Guide with eBook
$9.40 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Istanbul & Northwest Turkey Travel Reference Map WP
$9.89 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Istanbul, City map 1:10.000, City Pocket map + The Big Five
$11.92 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Collins Turkish Phrasebook and Dictionary Gem Edition (Collins Gem)
$0.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)DK Eyewitness Travel Guide Turkey (Eyewitness Travel Guides)
$12.11 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Rick Steves Istanbul: With Ephesus & Cappadocia
$15.21 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)The Amazing Mrs. Pollifax (Mrs. Pollifax Series Book 2)
$5.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)The Turkish Cookbook
$40.01 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Istanbul, City map 1:10.000, City Pocket map + The Big Five
$11.92 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Lonely Planet Turkey (Travel Guide)
$2.50 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Fodor's Essential Turkey (Full-color Travel Guide)
$16.60 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Time Out Istanbul
$2.20 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Learn Turkish in 100 Days: The 100% Natural Method to Finally Get Results with Turkish! (For Beginners)
$9.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Pearl River Delta China and Comparison with Turkey
Distance:
China PRD
- Hong Kong- Guangzhou: 119 km
- Zhaoqing-Huizhou: 200 km
Turkey Istanbul
- Gebze-Silivri: 109
- Bakırköy-Terkos: 40 km
- Kocaeli-Edirne: 300 km
Population:
- 65 million
The #PearlRiverDelta is the world’s largest conurbation. Growth has been unbelievable over the last two decades. buff.ly/2gvZFqJ
Pearl River Delta – Levent AĞAOĞLU (agaoglulevent.com)
DK Eyewitness Travel Guide Istanbul (Eyewitness Travel Guides)
$10.26 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Istanbul, City map 1:10.000, City Pocket map + The Big Five
$11.92 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Istanbul Travel Guide 2026: The Updated Companion to Experience Turkey's Best-Kept Secrets with Practical Itineraries, Detailed Maps, Bucket Hacks & Hidden Gems
$16.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Istanbul Travel Guide 2026: Top Places to Visit, Things to Do, Exploring Neighborhood, Itineraries, Festivals and Events, Food and Drink, Shopping, ... History And Culture. (EXPLORE THE GLOBE)
$13.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Istanbul Travel Guide 2025: Discover Istanbul’s Top Attractions, Hidden Gems, Cultural Highlights, Timely Itineraries, and Budget-Friendly Hacks for Every Traveler
$0.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)The Mini Rough Guide to Istanbul and the Aegean Coast: Travel Guide with eBook
$9.70 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)DK Top 10 Istanbul (Pocket Travel Guide)
$11.39 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Time Out Istanbul
$2.20 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Pocket Rough Guide Istanbul: Travel Guide with eBook
$9.40 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Modern Istanbul Map / Modern Istanbul Haritasi: Guide to Modern Architecture in Istanbul, Turkey (Blue Crow Media Architecture Maps)
$13.00 (as of 07/02/2026 22:15 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)The Turkish Cookbook
$40.01 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Turkey Travel Guide: Captivating Adventures through Rich History, Turkish Delights, Turkish Landmarks, Hidden Gems, and More (Traveling the World)
$13.69 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Istanbul, City map 1:10.000, City Pocket map + The Big Five
$11.92 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Learn Turkish in 100 Days: The 100% Natural Method to Finally Get Results with Turkish! (For Beginners)
$9.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Crescent and Star: Turkey Between Two Worlds
$6.49 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)DK Top 10 Istanbul (Pocket Travel Guide)
$11.39 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)A Guide to Biblical Sites in Greece and Turkey
$15.71 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Istanbul: City of Majesty at the Crossroads of the World
$4.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)High Albania
$0.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Collins Turkish Phrasebook and Dictionary Gem Edition (Collins Gem)
$0.99 (as of 07/02/2026 22:22 GMT +03:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Turkey and the Turks, by Justin Mc Carthy
https://www.tc-america.org/files/news/pdf/who-are-turks.pdf